Health benefits and the environmental repercussions
In recent years, there has been escalating attention to plant-based diets, for reasons of personal health and also for their environmental merits. A diet focused on plants puts a great deal of emphasis on foods derived from plants. In this regard, we’re regarding not only fresh fruits and vegetables, but also a wide array of essential products, including nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, legumes, and beans. Despite the fact that many people link plant-based diets with vegan or vegetarian lifestyles, the truth is there are several types, some of which allow for a little animal product intake. The focus of this article is on investigating how plant-based diets provide health benefits and what their influence is on the environment.
What is a Plant-Based Diet?

A diet centered on plants includes foods that develop from plants, notably a wide selection of fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. Despite the frequent use of the term in place of vegan or vegetarian diets, it doesn’t always rule out all animal products. Those on plant-based plans might eat little amounts of meat, fish, dairy, or eggs, but the majority of their nutrients derives from plants. and improve metabolism.
There are different types of plant-based diets, including:
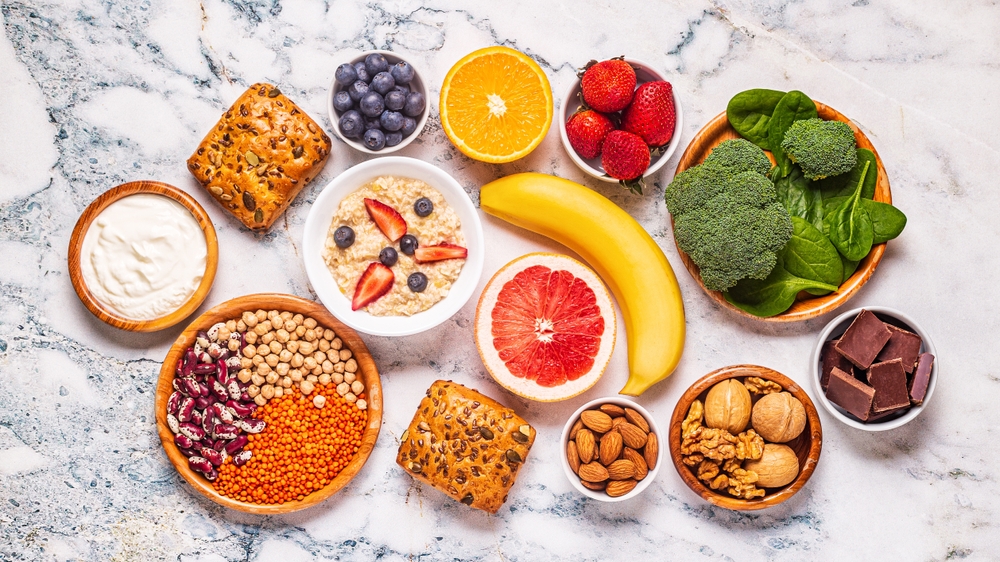

- Vegan – A nutritional plan that leaves out all items derived from animals, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey.
- Vegetarianism - A nutrition style that bypasses meat intake but may contain eggs and dairy products.
- Flexitarian - A mostly vegetable based diet that occasionally adds animal products is what we call Flexitarian.
- Pescatarian - A diet referred to as Pescatarian consists mainly of plants alongside seafood and fish.
- Every one of these diets has its own definition of how strictly to omit animal products, but the focus generally remains on plant-origin foods.
The Effective Benefits of a Diet Containing Plants

1. Nutrient-Rich Foods Plant diets are marked by a great number of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and fiber. Vitamins A, C, and E are essential to your diet, and they come from fruits and vegetables, which also provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and protein from whole grains and legumes. Vegetarian diets, on the other hand, normally rank low in saturated fats and cholesterol, which are widespread in products derived from animals.
2. Less chance of developing any diseases of which are categorized as chronic. A plant-based diet greatly enhances the ability to decrease the risks associated with chronic diseases. A large number of studies point to the fact that individuals on plant-based diets have a lower frequency of heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and several cancers. The high level of fiber found in plant foods helps to control blood sugar and cholesterol; meanwhile, the antioxidants lessen inflammation, which is vital for many chronic health problems.
Improved Heart Health
Heart disease is one of the leading factors in global deaths, with diet being critically important for its development. Because of their reduced levels of saturated fat and cholesterol, plant-based diets are related to better heart health. Analyses show that people who maintain a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle have a 25% lower likely hood of death from heart disease in comparison to carnivores. The plentiful amounts of fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants from plant foods are associated with improved cardiovascular and reduced blood pressure health.
Weight Management

Adequately maintaining one’s weight is important for total health, and plant-based diets can successfully help manage weight. Generally, lower-calorie plant foods are also enriched with fiber, which results in longer feelings of fullness. The results demonstrate that individuals who pursue a plant-based diet routinely have a lower BMI when compared to meat-eaters. This occurs, to some extent, because plant diets are of lower energy density, which allows for easier control of calorie intake since they house fewer calories gram for gram of food.
Better Digestion
A plant-rich diet full of fiber helps enhance both gut health and the digestive process. Fiber helps maintain regular bowel movements, stops constipation, and enhances helpful gut bacterial growth. Having nutritional balance in the gut correlates with an increased immune system, greater mental wellbeing, and a lowered chance of digestive illnesses, including IBS and diverticulitis.
Lower Cancer Risk
The association includes cancer variants such as colon, breast, and prostate with eating a lot of processed meats and animal products. Plant-based diets are, alternately, rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that help mitigate cell damage and fight cancer. Consuming plant-based fiber is important for predictable bowel movements, which may help lower the risk of colon cancer.
Longevity
People with plant-based diets have a tendency to have lives that are both healthier and longer. This is probably caused by the advantages of improved heart health, less chronic disease rates, and better weight management. Often, the diets in Blue Zones, locations with the longest living people, consist mostly of plants, particularly whole grains, beans, and vegetables.
Environmental ramifications of eating a plant-based diet
Throughout the world, animal product production ranks among the biggest sources of greenhouse gas emissions. The cultivation of livestock, especially cattle, creates considerable quantities of methane, an essential greenhouse gas that raises the global warming level. Alternatively, meals from plant-based sources usually showcase a much smaller carbon footprint. Research shows that moving towards a plant-based diet can help to cut an individual’s carbon footprint by up to 50%.
For animal farming, there’s a requirement for huge tracts of land for the animals along with the growers’ feed crops. In a different light, the cultivation of crops intended for direct human eating needs much smaller land areas. You need around 20 times more land to harvest a pound of beef than you do for a pound of vegetables. A diet centred on plants, by reducing meat consumption, can allow for the use of land toward new goals, including reforestation, which could better support actions to mitigate climate change.
The use of water is enormous in the field of animal agriculture. Producing one pound of beef needs thousands of gallons of water, mainly as a result of the water needed for feed growth. Generally speaking, plant foods, mostly grains and vegetables, call for comparatively less water for their cultivation. People who select a plant-based diet can remarkably cut down their water footprint, especially important in regions facing either water scarcity or drought.
The expansion of animal agriculture is affiliated with damage to habitat, deforestation, and a fall in biodiversity. The cutting down of forests for cattle ranching and the farmland for animal feed causes serious difficulties for wildlife. Keeping ecosystem integrity and conserving biodiversity via plant-based diets helps them to also lower their need for animal products. On the other hand, plant-based agriculture usually shows a smaller carbon footprint and is improbable to lead to habitat destruction.
The production of a lot of waste from animal farming, mostly manure, can result in both water pollution and damage to ecosystems within water. In addition, antibiotic application in livestock farming is contributing to antibiotic resistance, an increasing public health menace. The environmental sustainability model relies heavily on agricultural methods grounded in plant life, which fall quite behind in generating waste and pollution.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Diets rich in plants have a host of positives for individual health and the environment, even though they face a number of challenges in execution. The widespread belief is that diets that exclude animal products are necessarily healthier than those that include them. What is important to remember is that there are plant-based foods that aren’t nutritious. Vegan junk food and a variety of processed plant-based items may contain extra unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium.
One more challenge is to make certain that a plant-based diet offers all the needed nutrients. Vitamin B12 serves many vital functions including nerve function and the production of blood cells, but it abundantly resides in animal products. Those on plant-based diets may find they have to add supplements or consume nutrient-enriched foods to meet their dietary needs.
How should we make the shift to a plant-based diet?
For anyone wanting to adopt a plant-based eating style, doing it slowly is important. Kicking things off means starting with more plant-based meals on Monday, no meat included, and then slowly lessening your consumption of animal products. Take notice of vital meals rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Breaking the norm, give new recipes made with plant-based alternatives to common dishes a try.
On top of that, ensure that you educate yourself on correct nutrition to make sure you get all the vital vitamins and minerals. Plenty of plant-based diets can lack specific nutrients, including iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, so it’s important to find alternative plant sources for these nutrients or to think about supplementation.
Conclusion:
Diets centered around plants give several health advantages, such as improved heart function, improved digestion, and a diminished chance of chronic health problems. They serve to decrease our ecological outcomes by means of reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, an sustainable water usage, and the conservation of biodiversity. In spite of the challenges, effective planning combined with broadened knowledge can produce a healthful and sustainable plant-based diet choice for both individuals and our planet.
FAQs
A plant based diet mainly include food products that are derived from plants such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. It has the added bonus of being good for health and assisting in the sustainability of the earth. Here is our guide to some of the varieties of foods common in plant-base diets, what each product does for you, and ideas of how to best use them in your diet.
Indeed, a plant-based diet is indeed very healthy and advantageous for human health in all related ways. This dietary portfolio entails the use of entire, low processed foods obtained mostly from plants with an emphasis on vegetables and fruits, whole grain, pulses, nuts and seeds. Now, it is high time to describe the ranges of plant-based diet’s positive and negative impacts, as well as recommendations for its successful implementation.
Indeed, a plant-based diet is indeed very healthy and advantageous for human health in all related ways. This dietary portfolio entails the use of entire, low processed foods obtained mostly from plants with an emphasis on vegetables and fruits, whole grain, pulses, nuts and seeds. Now, it is high time to describe the ranges of plant-based diet’s positive and negative impacts, as well as recommendations for its successful implementation.


